Submitted to: Meteoritics and Planetary Science
FINAL DOI TO BE ASSIGNED AFTER REVISIONS AND FINAL PUBLICATION
Abstract:
Troilite is a common phase in iron meteorites, but there are limited data available for the partitioning behavior of elements between troilite and solid metal. In this study, we present the results of experiments with coexisting Fe-Ni solid metal, a S-rich metallic liquid, and troilite, conducted at 800–925°C in evacuated silica tubes at 1 atm. We report solid metal-troilite partition coefficients for 22 elements commonly studied in iron meteorites. We find that elements with chalcophile behavior have an affinity for troilite and that the majority of siderophile elements are incompatible in troilite. A notable exception to this generalization is for the siderophile element Mo, which partitions roughly equally between solid metal and troilite. We find that Ni and Co are largely concentrated in the solid metal, but given their higher concentrations in iron meteorites, their partitioning behavior indicates that measurable amounts of Ni and Co should be present in iron meteorite troilite when it forms. Our work motivates the need for additional measurements of the trace element composition of iron meteorite troilite and validates the assumption made in iron meteorite crystallization models that partitioning into troilite can be neglected for the majority of siderophile elements, with the exception of Mo.
| Preview | Filename | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
summary_massspecdata_jun2023.xlsx |
Excel sheet with data and calculations for each experiment |
|
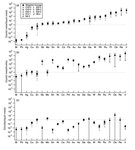
figure2_layoutpartitioncoefficients.jpg |
Figure 2 |

|
figure5_sm_tro_layoutv2.jpg |
Figure 5 |

|
figure6_meteorite_comparison_figurev2.jpg |
Figure 6 |
|
|
chabot_troilite2024-11.pdf |
Submitted Manuscript Text |
|
|
chabot_troilite_tables2024-08-27.docx |
Manuscript Tables |
|
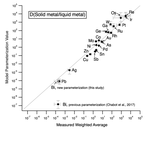
figure4_sm_lm_compare.png |
Figure 4 |
|
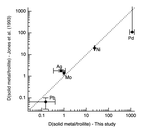
figure3_sm_troijan2025.png |
Figure 3 |
|
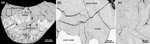
figure1_n8-3_semv2.png |
Figure 1 |
|
|
figure1_n8-3_semv2.psd |
Figure 1 - Photoshop |